Channel Tunnel (1880)
Channel Tunnel (1880)
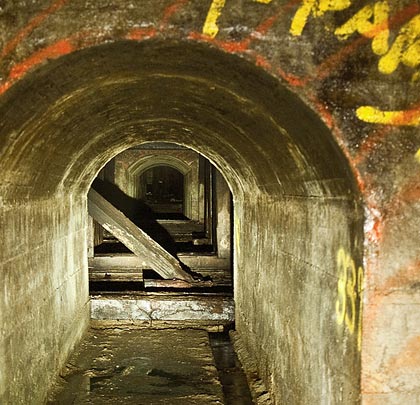
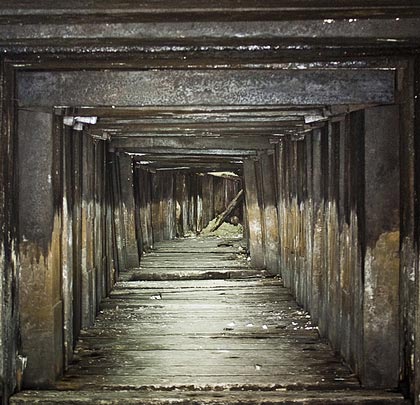



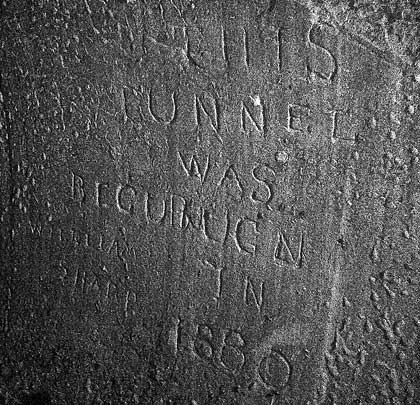






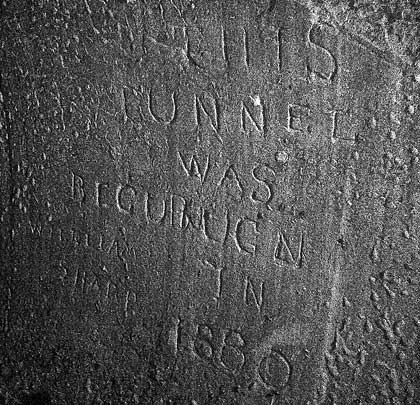



The idea of a fixed link across the English Channel was first put forward in the early part of the 19th Century but concerns over national security stalled attempts to progress it.
But an Anglo-French protocol was established in 1876 for a railway tunnel under the Channel. South Eastern Railway Chairman Sir Edward Watkin and French Suez Canal contractor Alexandre Lavalley conducted exploratory works on either side of the water, coming together in 1882 under the umbrella of the Submarine Railway Company.
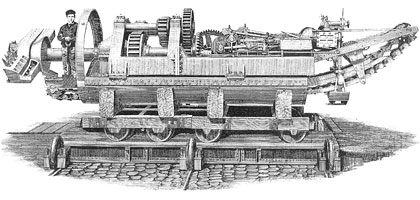
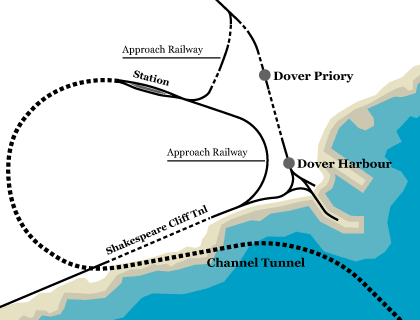
In 1880, No.1 shaft was sunk and a 7-foot diameter pilot tunnel begun below Abbot’s Cliff, between Dover and Folkestone, 10 feet above high water level. The driving force was Captain Thomas English’s rotary boring machine – 33 feet in length and powered by compressed air – which was capable of cutting 5/16″ for every rotation of its cutting head, at a rate of two revolutions per minute and almost half-a-mile per month. It was though hoped that this performance could be improved over time.
In February 1881, with about 800 feet driven and the machine proven, work was refocused at a site further along the coast, accessed via the 160-foot No.2 shaft at Shakespeare Cliff. Here another pilot tunnel was started under the foreshore, progressing through lower grey chalk towards a meeting with the French pilot tunnel – which was extending from Sangatte – 11 miles out to sea. This phase of the work was expected to be complete by 1886. Machinery was being developed which would then have enlarged the heading to 14 feet in diameter before a 2-foot thick concrete lining was inserted. The approach railways would fall on a gradient of 1:80 before reaching a depth of 150 feet below the sea bed. Operational ventilation would be provided by the compressed-air locomotives used to haul the trains.
But 1882 saw the government call a halt, worried about the military implications of a land-link to Europe. Sir Edward’s well-reasoned reassurances fell on deaf ears with 2,040 yards of the Shakespeare Cliff heading driven, another 897 yards at Abbot’s Cliff and 1,825 yards on the French side of the Channel. Both shafts were later backfilled.
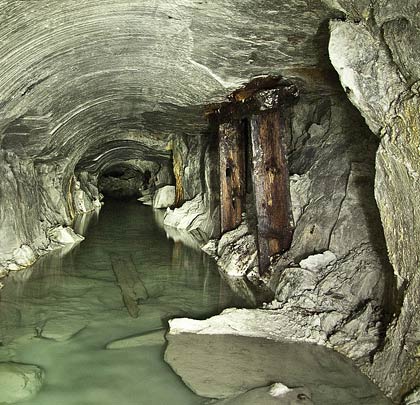
When the idea of a tunnel was revisited in both 1974 and 1988, various remedial works were carried out on the 1880s workings as a result of the new alignments potentially intersecting with them. This work discovered a number of roof falls and broken timber supports. A concrete bulkhead was installed 890 yards into the No.2 heading, effectively entombing the boring machine.
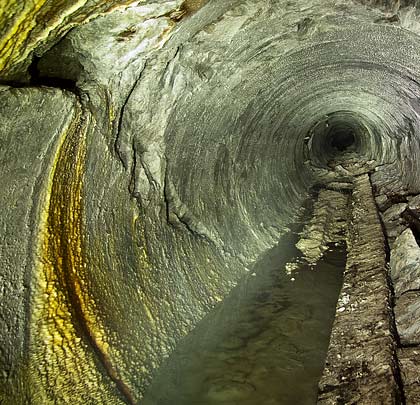
Access to the original heading has been maintained as it meets one of the drainage adits driven from the base of the cliff under the coastal railway. This joins the 1880 tunnel 70 metres from the surface, after passing beneath Shakespeare Cliff Tunnel where it has been reinforced with concrete arches. Adjacent to the junction is a timber-lined passage leading to the base of the shaft where the boring machine would have been assembled.
Initially, the pilot tunnel remains in reasonable condition. After 85 yards a much-photographed message was inscribed on the left-hand wall by William Sharp, presumably one of the miners involved in the work, recording the start of work in 1880. Thereafter the gradient steepens and the flood waters become deeper, eventually reaching about 3 feet. Some timber propping is provided on the right-hand side but, despite this, a number of chalk falls have occurred, including one that is almost roof height.
Click here for more of Locations Photography’s pictures.
 March 2012
March 2012